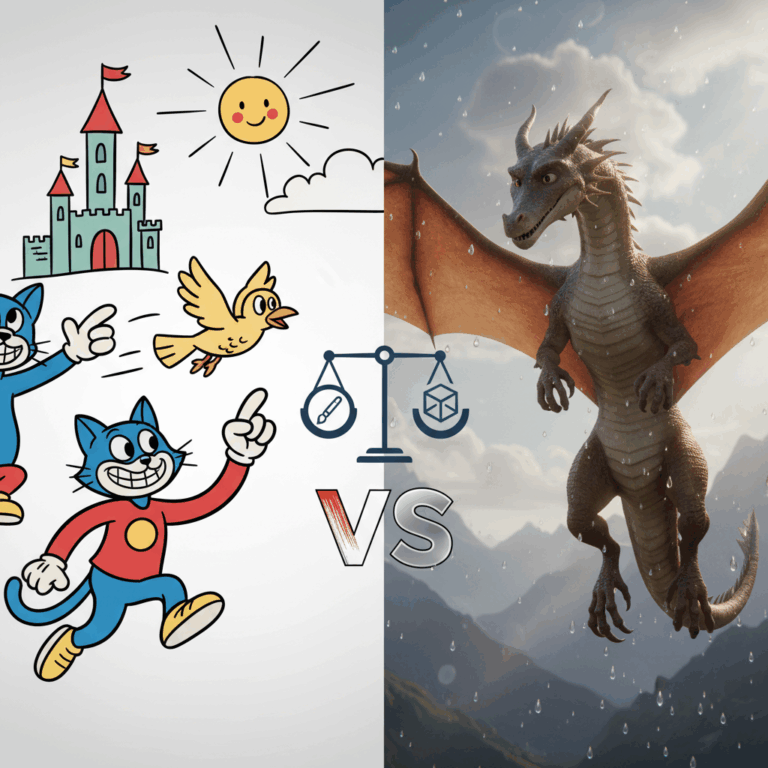
Main differences between 2D and 3D animation
The 2d animation it is based on flat images with two dimensions: height and width, creating a more stylized and artistic effect.
In contrast, the 3d animation add depth, using three-dimensional models that offer realism and visual detail.
Both techniques have different processes and tools that influence the production and final result of the animation.
Perception of depth and dimension
The 2D animation presents a two-dimensional space without depth, which gives a flat but expressive and stylized appearance.
On the other hand, 3D animation uses models with depth that allow realistic visual effects, such as shadows and camera movements.
This facilitates a more immersive experience, ideal for scenarios that require volume and visual realism.
Production processes and tools
In 2D, each frame is usually drawn by hand or with specialized software, requiring traditional artistic skills.
3D animation involves modeling and animation in virtual environments, using advanced programs and hardware to create reusable objects.
While 2D is usually faster and cheaper, 3D demands greater investment, learning time and technological equipment.
Specific advantages of each technique
2D animation offers more agile and economical production, ideal for projects with time and budget constraints.
In addition, it allows great artistic freedom that favors expressive styles and symbolic or fantastic narratives.
Benefits and applications of 2D animation
2D animation is recognized for its lower cost and relative speed in production, facilitating the making of series and short films.
Its flat, expressive style is perfect for independent video games and projects that require an artistic and cartoonish aesthetic.
This makes it widely used in products where simplicity and visual creativity are priorities over realism.
Advantages and uses of 3D animation
3D animation stands out for its ability to achieve impressive visual realism through depth and volumetric details.
It allows models to be reused and animated from multiple angles, offering great flexibility for film productions or advertising.
Although it requires greater investment, it is ideal for projects that demand impressive visual effects and realistic simulations.
Characteristic visual styles
The visual style of 2D animation is characterized by its flat appearance, bright colors and defined lines that highlight expressiveness.
In contrast, 3D animation offers a volumetric style with shadows, textures and depth that simulate reality.
Both styles have unique qualities that influence the perception and visual impact of animated productions.
Features of the 2D style
2D animation stands out for its flat and expressive graphics, where each frame emphasizes design and artistic creativity.
Colors tend to be bright and simple, favoring a cartoonish or stylized look that connects with symbolic emotions.
This style is ideal for telling abstract and fantastic stories, since it does not depend on visual realism but on visual interpretation.
Visual simplicity facilitates clear and direct communication, increasing accessibility for different audiences.
Features of the 3D style
In 3D animation, the style is based on creating objects and characters with realistic depth, volume and textures.
Shadows, lighting and camera movements are used to generate an immersive and dynamic visual environment, very close to reality.
This approach allows complex details and sophisticated visual effects to be represented, increasing the spectacular nature of the animation.
The 3D style is preferred in productions that seek a high degree of realism or a striking and modern visual impact.
Factors to choose between 2D and 3D animation
The choice between animation 2D and 3D it depends on the artistic and narrative objectives that the creator seeks to achieve.
The availability of technical and human resources also influences, as well as the complexity of the proposed project.
Evaluating these factors is key to defining the most appropriate technique for each audiovisual production.
Artistic and narrative objectives
2D animation is ideal for stories that require an expressive, symbolic or cartoonish style, where visual creativity predominates.
Instead, 3D animation favors narratives that seek realism, depth, and impressive visual effects for greater immersion.
The decision is based on how you want to tell the story and what type of visual experience you want to provoke in the viewer.
Available resources and technical complexity
2D animation typically requires fewer technical resources and can be produced with a smaller budget and basic equipment.
In contrast, 3D animation demands specialized software, powerful hardware, and longer production time for modeling and animating.
Additionally, it is necessary to consider the team's experience, since 3D involves a higher learning curve.